EmbeddingFourier for Ultra-High-Definition
Low-Light Image Enhancement
Nankai University
Abstract
Ultra-High-Definition (UHD) photo has gradually become the standard configuration in advanced imaging devices. The new standard unveils many issues in existing approaches for low-light image enhancement (LLIE), especially in dealing with the intricate issue of joint luminance enhancement and noise removal while remaining efficient. Unlike existing methods that address the problem in the spatial domain, we propose a new solution, UHDFour, that embeds Fourier transform into a cascaded network. Our approach is motivated by a few unique characteristics in the Fourier domain: 1) most luminance information concentrates on amplitudes while noise is closely related to phases, and 2) a high-resolution image and its low-resolution version share similar amplitude patterns. Through embedding Fourier into our network, the amplitude and phase of a low-light image are separately processed to avoid amplifying noise when enhancing luminance. Besides, UHDFour is scalable to UHD images by implementing amplitude and phase enhancement under the low-resolution regime and then adjusting the high-resolution scale with few computations. We also contribute the first real UHD LLIE dataset, UHD-LL, that contains 2,150 low-noise/normal-clear 4K image pairs with diverse darkness and noise levels captured in different scenarios. With this dataset, we systematically analyze the performance of existing LLIE methods for processing UHD images and demonstrate the advantage of our solution. We believe our new framework, coupled with the dataset, would push the frontier of LLIE towards UHD.
Dataset

We collect a real low-noise/normal-clear paired image dataset that contains 2,150 pairs of 4K UHD data saved in 8bit sRGB format. Images are collected from a camera mounted on a tripod to ensure stability. Two cameras, a Sony $\alpha7$ camera and a Sony Alpha a6300 camera, are used to offer diversity. The ground truth (or normal-clear) image is captured with a small ISO in [100,800] in a bright scene (indoor or outdoor). The corresponding low-noise image is acquired by increasing the ISO in [1000,20000] and reducing the exposure time. Due to the constraints of exposure gears in the cameras, shooting in the large ISO range may produce bright images, which opposes the purpose of capturing low-light and noisy images. Thus, in some cases, we put a neutral-density (ND) filter with different ratios on the camera lens to capture low-noise images. In this way, we can increase the ISO to generate heavier noises and simultaneously obtain extremely dark images, enriching the diversity of darkness and noise levels.
Method
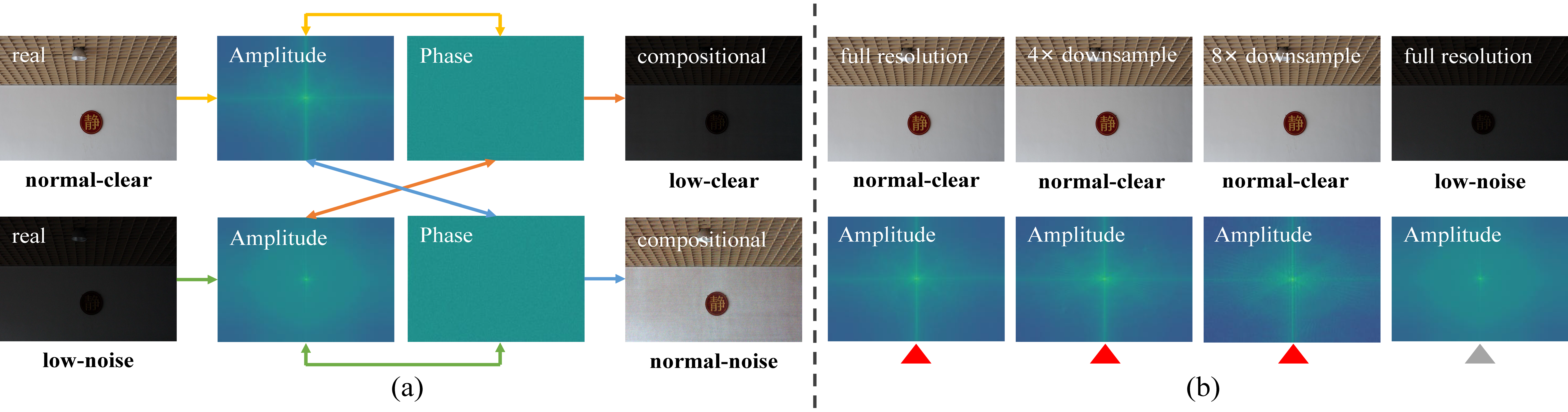
We observed that (a) luminance and noise can be `decomposed' to a certain extent in the Fourier domain and (b) HR image and its LR versions share similar amplitude patterns. The amplitude and phase are produced by Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) and the compositional images are obtained by Inverse FFT (IFFT). For visualization, we show the amplitude and phase in imagery format with common transformations. Lines of the same color indicate a set of FFT/IFFT transforms. The red triangles mark the similar pattern (obviously different from the gray one).
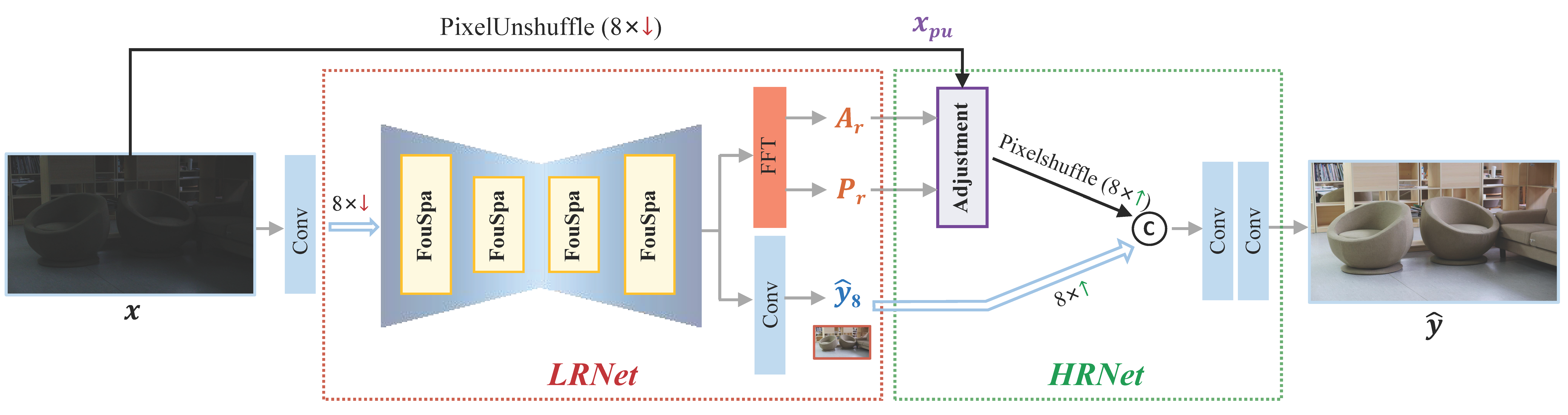
Our approach consists of an LRNet and an HRDNet. The LRNet is an encoder-decoder network that produces 8$\times$ downsampled result $\hat{y_{8}}$ and the refined amplitude $A_{r}$ and phase $P_{r}$ features. We omit the skip connections for brevity. The HRNet contains an Adjustment Block and the upsampling operation, producing the final result $\hat{y}$. Most computation is conducted in the LRNet.
Results

We use the released model directly in this evaluation. All released models cannot handle the UHD low-light image well.

All compared models leave noise, artifacts, or color deviations in the results. Our method achieves a visually pleasing result.
License
We retain all the copyrights of this method.
Citation
If you find our dataset and paper useful for your research, please consider citing our work:
@inproceedings{UHDFourICLR2023,
title={EmbeddingFourier for Ultra-High-Definition
Low-Light Image Enhancement},
author={Chongyi Li and Chun-Le Guo and Man Zhou and Zhexin Liang and Shangchen Zhou and Ruicheng Feng and Chen Change Loy},
booktitle={ICLR},
year={2023}
}
Contact
If you have any question, please contact us via lichongyi25@gmail.com.

