
lichongyi25 @ gmail.com
[GitHub]
[DBLP]
[Google Scholar]
Nested Network with Two-Stream Pyramid for Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images
Introduction:
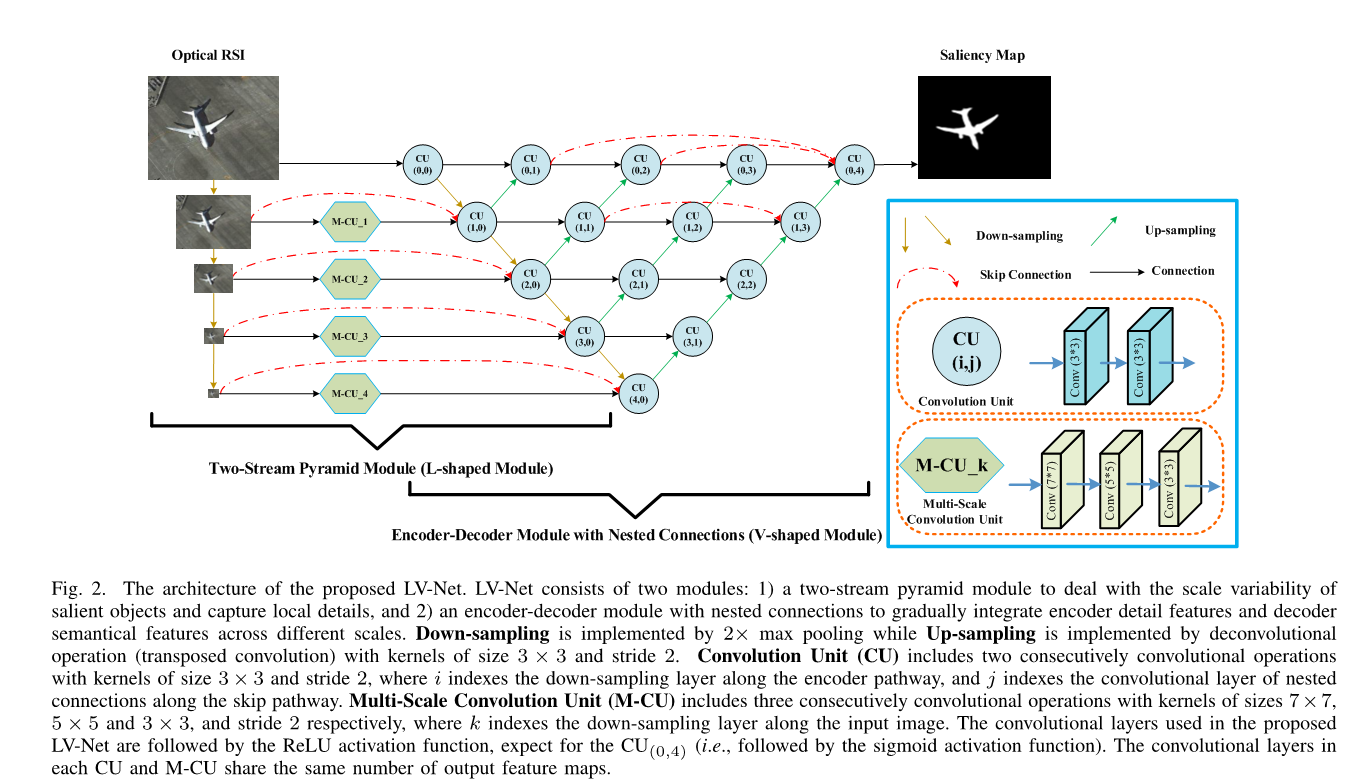
Arising from the various object types and scales, diverse imaging orientations, and cluttered backgrounds in optical remote sensing image (RSI), it is difficult to directly extend the success of salient object detection for nature scene image to the optical RSI. In this paper, we propose an end-to-end deep network called LV-Net based on the shape of network architecture, which detects salient objects from optical RSIs in a purely data-driven fashion. The proposed LV-Net consists of two key modules, i.e., a two-stream pyramid module (L-shaped module) and an encoder-decoder module with nested connections (V-shaped module). Specifically, the L-shaped module extracts a set of complementary information hierarchically by using a two-stream pyramid structure, which is beneficial to perceiving the diverse scales and local details of salient objects. The V-shaped module gradually integrates encoder detail features with decoder semantic features through nested connections, which aims at sup- pressing the cluttered backgrounds and highlighting the salient objects. In addition, we construct the first publicly available optical RSI dataset for salient object detection, including 800 images with varying spatial resolutions, diverse saliency types, and pixel-wise ground truth. Experiments on this benchmark dataset demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art salient object detection methods both qualitatively and quantitatively.
Paper:
Chongyi Li, Runmin Cong, Junhui Hou, Sanyi Zhang, Yue Qian, and Sam Kwong, Nested Network with Two-Stream Pyramid for Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images. PDF (TGRS, 2019)
LV-Net Resutls:
[Google Drive Link]
[Baidu Cloud Link]
ORSSD Dataset:
[Google Drive Link]
[Baidu Cloud Link]
If you need the this dataset, please cite the related paper. Thanks.